- Home
- Growth Hormone
- Growth Hormone
- Growth Hormone Deficiency
- Growth Hormone Therapy
- Growth Hormone Injections
get startedThe Most Effective Hormone Replacement TherapiesHow to Inject Testosterone. Dosages and Administration of Injectable Testosterone
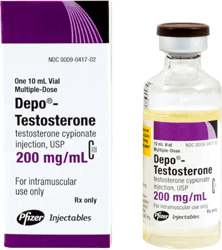
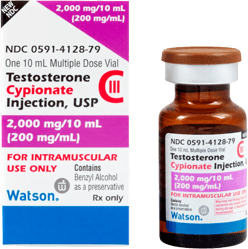
- The most common form of testosterone therapy is testosterone cypionate, also known as DEPO-testosterone.
- The most effective form of DEPO-testosterone is given via intramuscular injection.
- When given correctly testosterone injections are relatively painless, and free from any major side effects.
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is usually given via injection. Do not be concerned if you have a fear of needles. Learning how to give yourself the shot is not hard, but it is important to do it right to avoid side effects or adverse reactions. This page will provide an overview of what every man needs to know about self-administration of testosterone injection. It is not meant to be a substitute for instructions from a health professional.
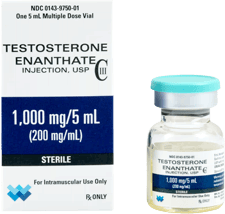
Injectable hormone therapy for men is prescribed on a very individualized basis. Therefore, dosages of TRT injections will vary. The most common form of TRT injections contains testosterone cypionate. This medication is often referred to as “DEPO-Testosterone” or merely “DEPO.
This form of TRT is usually prescribed in vials of 100 mg/mL solution or 200 mg/mL solution.
Each mL of the 100 mg/mL solution contains:
- Testosterone cypionate (TC)……………..100 mg
- Benzyl benzoate……………..0.1 mL
- Cottonseed oil……………..736 mg
- Benzyl alcohol (as preservative)……………..9.45 mg
Each mL of the 200 mg/mL solution contains:
- TC…………….……………. 200 mg
- Benzyl benzoate……………..0.2 mL
- Cottonseed oil……………..560 mg
- Benzyl alcohol (as preservative)……………..9.45 mg
There are two testosterone injection methods. Hormone replacement therapy for men is most commonly given via intramuscular injections. However, some patients could be prescribed subcutaneous injections. Your healthcare provider will determine which type of injection of testosterone is right for you.
The most common form of injectable testosterone therapy contains testosterone cypionate which is the oil-soluble 17 (beta)-cyclopentylpropionate ester of the androgenic hormone testosterone. This is commonly referred to as “DEPO-Testosterone” or merely “DEPO”.
How to Give a Testosterone Shot
Studies have found that the effectiveness of your injection is not influenced by the time of day. However, it is very important that you learn where to give your testosterone shot and understand all sterile techniques.
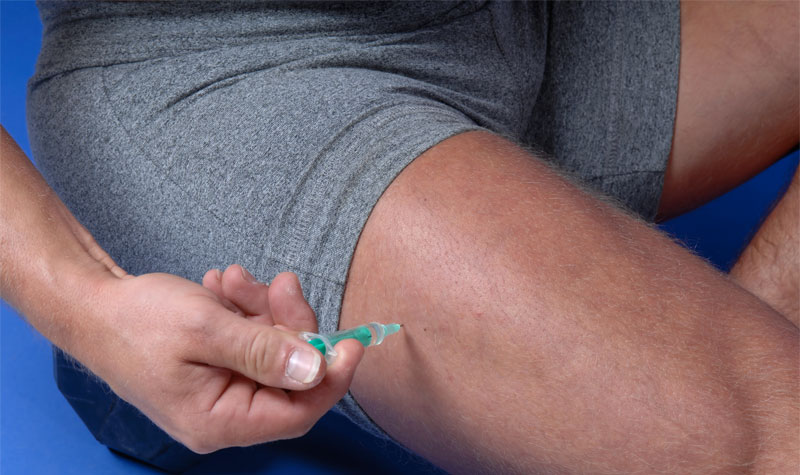
Male hormone shots are usually given via intramuscular injection. Intramuscular (IM) injections are given deep into the muscles. The very vascular muscles of your arm, your upper thigh, or the “glutes” are the most common injection sites. The needles used to deliver male hormones are very thin, much like the ones diabetics use to deliver insulin. It should not take you a long period of time to learn how to take your shots. Once you learn how to give yourself your injections, you will find them easy to do and quite painless.
Testosterone is given via intramuscular injection. Intramuscular (IM) injections are given deep into the muscles. The very vascular muscles of your arm, your thigh, or the “glutes” are the most common injection sites.
Your approved dosage of TRT should be administered like any other intramuscular injection. Intramuscular shots are given at a 90-degree angle, using a sterile, never-before-used needle. The needle size used for IM injections is usually 22-23 Gauge, 1-1.5 inches in length.
Basically, there are four steps to giving yourself an intramuscular injection of male hormones.
Step 1: Setting Up for the Injection
Preparing for your injection of medicine starts by finding a clean and comfortable work area that you will use each time you administer your testosterone injections. Make sure your medication is at room temperature. Look in the vial and check for any discoloration or particles in the fluid. Check the expiration date on the medication bottle. Do not use a vial of with anything floating in the suspension or that is discolored or expired. Wash your hands with soap very well. Using antibacterial soap is the best way to reduce the risk of infection at the injection site. Make sure you have a suitable needle on hand.
Step 2: Selecting and Preparing the Testosterone Injection Site
Again, your shot is most often given in the deep muscle. Most users choose the thigh, as it is one of the easier injection sites to use. Generally speaking, the areas with more muscle and less subcutaneous fat tend to be the least painful injection sites for hormone shots. However, wherever you choose to give your injections, it is best to rotate or alternate sites every other injection or so to avoid pain, inflammation, and other possible complications.
Step 3: Preparing the Testosterone Injection Dose
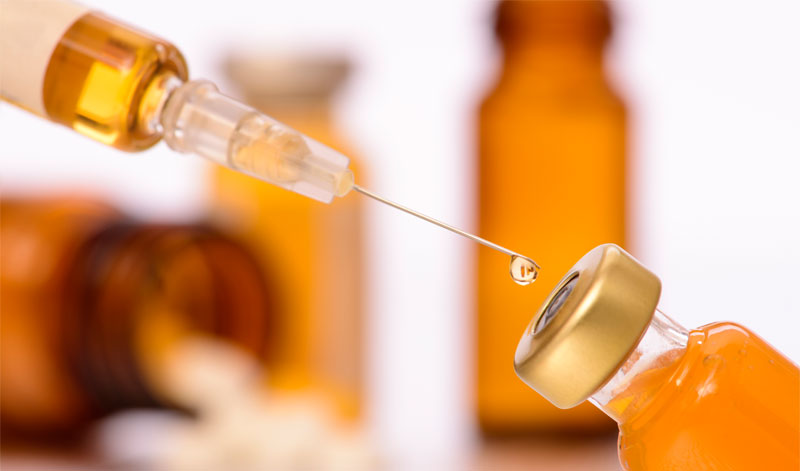
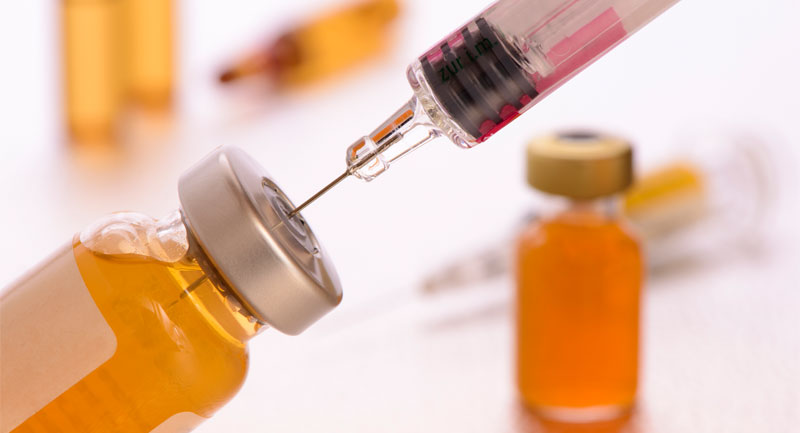
Take the cap off the vial. Clean the rubber stopper with one of the alcohol wipes included in your injection kit. The typical needle size to give the testosterone shot is a gauge of between 22 and 25. Some users suggest that you should use one needle to draw the medication into the syringe, discard that needle, and then use another to give yourself the actual injection. The rationale behind this is that the tip of the needle could get blunted by pushing it through the stopper of the vial and, therefore, possibly cause a more painful injection. There is nothing wrong with this practice; however, there is also little evidence to suggest that it is true. From a convenience standpoint, using a larger needle to draw up the liquid can be easier & faster, but ultimately, the choice is yours.
Step 4: Giving the Testosterone Injection
Place the vial on your clean flat working surface. Insert the needle straight down through the center of the rubber stopper. Keeping the needle in the vial, turn the vial upside down. With the needle still in the vial, check for air bubbles. If there are air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your fingers until the air bubbles rise to the top of the syringe. Then, slowly push the plunger up to force the air bubbles out of the syringe without removing the needle from the bottle. Pull the medication into the syringe only to the line that corresponds to your prescribed dosage.
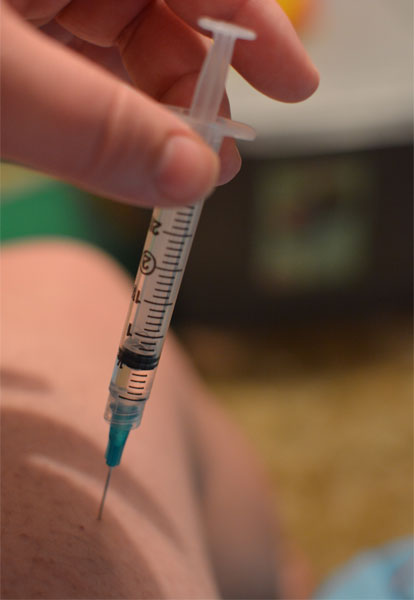
Clean the injection site skin with an alcohol swab; let it air dry. Stretch the skin flat using your fingers and thumb of one hand. Stick the needle into the muscle at a 90-degree angle with one quick and firm motion. Pull back slightly on the plunger of the syringe to check for blood; if you see blood, DO NOT proceed with the injection. If there is no blood in the needle, you can complete the injection by pushing the medication slowly into the muscle. After injection of the medication, rub the injection site in a circular motion to evenly disperse the medication and minimize swelling and soreness.
When you have completed all of the above steps, dispose of your used needle in a sturdy, puncture-proof container.
Subcutaneous Versus Intramuscular Testosterone Injections
Both subcutaneous and intramuscular injections deliver your dose of the medication into the body. They both provide similar effects of TRT, but there are some differences between the two types of injections. They differ in injection site, technique, absorption rate, and overall comfort. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their similarities and differences, as well as determining factors for choosing each method.
Steps Shared Between Subcutaneous and Intramuscular Injections
-
Preparation:
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water to prevent infection.
- Gather all necessary supplies: medication vial, syringe, alcohol swabs, a sharps disposal container, and gloves (optional but recommended for extra hygiene).
- Inspect the vial for clarity and expiration date. Avoid using it if it appears cloudy or past its expiration.
-
Drawing the Medication:
- Clean the vial’s rubber stopper with an alcohol swab.
- Insert the syringe needle into the vial and pull back to draw the correct dose.
- Remove any air bubbles by tapping the syringe and pressing the plunger slightly until only medication is at the tip.
-
Injection Site Cleaning:
- Clean the injection site (either the fatty tissue for subcutaneous or the muscle for intramuscular) with an alcohol swab.
- Let the area dry to reduce stinging during the injection.
-
Post-Injection Care:
- Dispose of the syringe in a sharps container.
- Apply pressure and possibly a small bandage to the injection site if there is minor bleeding.
Differences Between Subcutaneous and Intramuscular Injections
Subcutaneous Injections
-
Injection Site:
- Administered into the fatty tissue, typically in the abdomen, just above the belly button or the outer thigh.
- The needle is inserted at a 45-degree angle, aiming for the fat layer just under the skin.
-
Needle Type:
- Shorter needles (usually 26-30 gauge and 5/16 to 1/2 inch) are used, which may make this method more comfortable for some patients.
-
Absorption and Release:
- Absorption is generally slower with subcutaneous injections than with intramuscular injections. This can lead to a steadier release and potentially more stable levels of the medication in the blood.
- Subcutaneous injection also allows for more frequent injections, should your symptoms require you to take your shots more often.
-
Special Considerations and Care:
- Reduced Injection Pain: Subcutaneous injections are often less painful because they don’t penetrate the muscle.
- Reduced Risk of Bleeding: There is generally less bleeding or bruising compared to intramuscular injections.
- Potential for Local Irritation: Some people may experience irritation or lumps in the fatty tissue. Rotating injection sites can help mitigate this.
-
Who May Benefit:
- Individuals who are sensitive to needle pain.
- Patients who require smaller, more frequent doses.
Intramuscular Injections
- Injection Site:
- Administered directly into the muscle, commonly in the gluteus (buttocks) or deltoid (shoulder).
- The needle is inserted at a 90-degree angle to ensure it reaches the muscle.
- Needle Type:
- Longer and thicker needles (usually 20-25 gauge and 1-1.5 inches) are required to penetrate muscle tissue, which can be more uncomfortable.
- Absorption and Release:
- This medication tends to be absorbed faster in muscle, potentially leading to a quicker onset of its positive effects.
- However, this may also lead to greater fluctuations in testosterone levels, especially with less frequent dosing.
- Special Considerations and Care:
- Higher Pain Levels: Intramuscular injections can be more painful due to the thickness of the needle and muscle penetration.
- Increased Risk of Bleeding: Muscle tissue contains more blood vessels, which may lead to more post-injection bleeding or bruising.
- Risk of Nerve Damage: There is a small risk of hitting a nerve, especially if injected in the wrong location. This makes precise technique and site selection important.
- Who May Benefit:
- Individuals who require larger doses at longer intervals.
- Those who need faster onset or higher peak levels.
- Patients with higher muscle mass may tolerate and benefit more from intramuscular administration.
Choosing Between Subcutaneous and Intramuscular Injections
- Dosage Requirements:
- Higher Doses: Patients needing higher doses may be better suited to intramuscular injections for quicker and more efficient absorption.
- Lower, More Frequent Doses: Subcutaneous injections may work well for those on lower doses or smaller, more frequent doses for steady levels.
- Comfort and Tolerance:
- Pain Sensitivity: Patients sensitive to pain may prefer subcutaneous injections due to the shorter, thinner needle.
- Ease of Self-Administration: Subcutaneous injections are generally easier to self-administer due to more accessible injection sites and easier technique.
- Physician or Personal Preference:
- Some healthcare providers may prefer one method over the other based on experience, patient outcomes, or the patient’s medical history.
- Personal preference also plays a role, as some people may find one method less intimidating or easier to perform.
- Frequency of Injections:
- Subcutaneous injections can be done more frequently with fewer side effects, making them ideal for patients on more frequent dosing schedules.
- Intramuscular injections may be better for less frequent, larger doses, though they often require assistance from a healthcare professional.
Each injection method has its pros and cons, and the choice largely depends on your individual needs, comfort level, and your healthcare provider’s recommendation.
Does Administering Injectable Testosterone Hurt?
If you have a fear or phobia of needles, do not worry! When done correctly, taking injectable medications should not hurt. Still, some men report discomfort when taking their injections. Here are a few ways to reduce potential pain. The most important thing to consider is where you give the shot. Selection of your injection site is critical to minimizing discomfort.
Your injections should be given deeply into vascular muscle tissue. The deltoids, the vastus lateralis, and the gluteal muscles are the most common intramuscular (IM) injection sites. Those are your arm, thigh, and buttocks, respectively. Some of these sites are more prone to pain than others. Generally speaking, the areas with more muscle and less subcutaneous fat tend to be the least painful injection sites. The needles that are manufactured today are made with extraordinary sharpness and precision that allow them to be relatively painless, as compared to the injection methods of the past.
Regardless of where you choose to give your injections, it is best to rotate or alternate sites every other injection or so to avoid injection site pain, inflammation, and other possible complications.
Other Considerations
Other than how to administer your testosterone shot, there are a few other things you need to consider to minimize injection side effects, such as:
- Needle size in terms of length and gauge
- The volume of your dose
- Your particular injection technique
- To massage or not to massage
If it is possible to split your injections into more frequent, smaller dosages, less volume of medication in each injection can result in less pain.
As far as technique, to minimize the pain of your injection, keep the needle straight, and the faster you inject usually means less pain.
Because there are different types of testosterone in the various brands of injections, and there is some variation on how they work, some should be massaged in after they are injected, and some should not be. Consult the literature that comes with your injection kit or ask your prescriber if your particular type needs to be massaged in or not.
What Kind of Results Can I Expect From Testosterone Injections?
While taking your TRT correctly will minimize discomfort and maximize results, there are a few other things you need to understand about the results of TRT.
Number one, TRT is most successful when it is prescribed for your particular individual needs, lifestyle, and metabolism. As such, no two TRT patients will have an identical experience. Your results will be tailored to meet your unique goals and lifestyle.
The other thing you need to understand about hormone therapy for men is that while you will see results, you will not suddenly have the physique of Superman after your first injection. The whole reason why male hormone injections are to be taken over the course of a few months is that their effects are cumulative and take time to be achieved. Be patient. You will see results very soon!
Are There Any Risks to Testosterone Injections?
If you follow the tips and techniques stated above of how and where to administer your TRT, your injections should be relatively painless and risk-free.
Like any kind of therapy or medical treatment, however, injectable TRT does have some potential side effects.
The most common side effects of testosterone injections include:
- Injection site reactions or injection site soreness
- Acne
- Headache
- Loss of hair on the head
- Breast enlargement
- Oily skin
Risks Vs Benefits of Testosterone Shots
For most patients, the many positive benefits you will get from hormone replacement far outweigh any potential risks.
The benefits you can expect from TRT include:
- Increased strength
- Increased stamina
- More energy
- Increased ability to burn fat and build muscle
- Weight loss
- Healthier skin and bones
- Increased sexual drive
- Improvement with erectile dysfunction
- Lower LDL cholesterol levels
- Improved mental sharpness
As we hope you now can see, taking testosterone shots is nothing to be afraid of. In fact, hormone replacement therapy for men can be life-changing! Contact Us and find if TRT is right for you.
The needles used to deliver low testosterone treatments are very thin, much like the ones diabetics use to deliver insulin. Once you learn how to give yourself your testosterone injections, you will find them easy to do, and quite painless.
read this next
How To Administer Growth Hormone Injections
When given properly, growth hormone injections have been clinically proven to be the safest and most effective way to treat growth hormone deficiency (GHD).…read moreWhat are the side effects of Testosterone injections?
It is normal to wonder about the side effects of testosterone injections. However, you should not let concern about testosterone injection side effects, keep…read moreIs There a Best Time Of Day To Take Growth Hormone Injections?
Growth hormone therapy is the safest and most effective way to treat men or women suffering from a growth hormone deficiency. The only way…read moreHow is Growth Hormone Therapy Administered?
Genuine growth hormone therapy is administered one way, and only one way, via subcutaneous injections. Any other product that purports to be or contain…read more - Growth Hormone Therapy