- Home
- Growth Hormone
- Growth Hormone
- Growth Hormone Deficiency
- Growth Hormone Therapy
- Growth Hormone Injections
get startedThe Most Effective Hormone Replacement TherapiesWhat Are The Clinical Guidelines for Growth Hormone Deficiency in Adults
- Growth hormone deficiency in adults can cause a number of health issues.
- The proper dose of growth hormone therapy is based on a number of factors, other than height, weight, age and gender.
- Growth hormone therapy is a safe and effective treatment for adults with growth hormone deficiency (GHD).
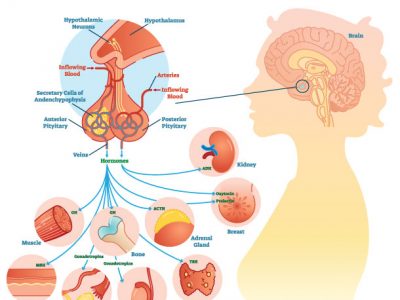
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD) is a recognized clinical condition by the medical establishment. GHD in adults most commonly persists from an untreated or ineffectively treated growth hormone deficiency in childhood. However, it can also develop in adulthood without any previous history of GHD.
Either way, the guidelines for adults with growth hormone deficiency suggest that unless it is well-established through the patient’s medical history that there is a known genetic disorder or damage, injury, or cancer to the pituitary gland, that has existed since childhood, a diagnosis of GHD needs to be confirmed through specific stimulation testing.
Growth hormone deficiency in adults can cause a number of health issues. According to the clinical guidelines for GHD, the chief complaint is an alteration of “body composition,” as the patient with GHD will present with increased fat mass and decreased muscle mass. Further, the ability to exercise effectively is reduced, cholesterol levels may be increased, as is the risk of a cardiovascular incident, such as heart attack or stroke. Other signs and symptoms listed in the guidelines for adults with GHD include:
- Decreased sweating and poor thermoregulation
- Increased insulin resistance
- Increased cholesterol
- Increase build-up of cardiac plaque
- Mood swings, increased anxiety and depression
- Drop in energy levels
- An overall sense of being unwell
The treatment recommended in all guidelines for adults with growth hormone deficiency is human growth hormone (HGH) replacement therapy. The guidelines suggest that HGH therapy improves the quality of life of adults with GHD by:
- Benefiting body composition
- Increasing exercise capacity
- Improving skeletal integrity
Most guidelines for administering growth hormone therapy for adults, state that the risks of dangerous side effects associated with HGH replacement are low. Guidelines also state that growth hormone therapy dosages should be tailored to an individual’s needs and lifestyle.
While there are guidelines set forth for treating adults with GHD, any final decision to prescribe growth hormone therapy should be made with careful evaluation of, and discussions with the specific patient.
Growth hormone deficiency in adults can cause a number of health issues. According to the clinical guidelines for GHD, the chief complaint is an alteration of “body composition,” as the patient with GHD will present with increased fat mass and decreased muscle mass.
Endocrine Society Guidelines for Growth Hormone Deficiency in Adults
Endocrinology is the medical specialty that most often treats adults with GHD. Endocrinologists specialize in glands and hormonal conditions and hormone imbalances caused by improperly functioning glands of the endocrine system. The American Society of Endocrinologists lists the following Guidelines for growth hormone deficiency in adults:
- An individual who has undergone treatment for childhood GHD, needs to be retested and revaluated for adult GHD once they have achieved full height, to see if they are continued candidates for growth hormone therapy, unless known damage or defect that will continue to reduce HGH production into adulthood is present.
- Adults who have had hypothalamic/pituitary disease, surgery or radiation treatments to these areas, head trauma, or have shown evidence of other decreased pituitary functions, should be tested for adult onset growth hormone deficiency.
- Because the spontaneous occurrence of GHD in adults is relatively uncommon, more than a single test is suggested before an accurate diagnosis of adult onset GHD can be made. It is recommended that in addition to an HGH stimulation test, an IGF-1 stimulation test is also made.
- Other tests that can be used to establish adult GHD include: the insulin tolerance test (ITT), the GHRH-arginine test and the glucagon stimulation test.
- A result of a normal IGF-1 test, should not be used to exclude a diagnosis of adult GHD but indicates other testing methods may be required.
- A pituitary axis is the complex interaction between the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus that directly influences certain biological processes. If a patient presents with 3 or more pituitary axes that are dysfunctional, there is strong evidence to suggest a growth hormone deficiency.
- Dosages for growth hormone therapy are not based on height or weight standards, and should be prescribed per individual needs. Patients should be started at the lowest effective dose, and regimens should be titrated (increased) based on response.
- Patients need to be closely monitored during growth hormone therapy, and testing for HGH levels and IGF-1 levels should be done semi-annually.
Dosages for growth hormone therapy are not based on height or weight standards, and should be prescribed per individual needs. Patients should be started at the lowest effective dose, and regimens should be titrated (increased) based on response.
Guidelines for Treatment of Adult Growth Hormone Deficiencies
In addition to the growth hormone deficiency guidelines listed above, there are specific guidelines for the treatment of growth hormone deficiency in adults.
Treatment guidelines for adults with GHD suggest that growth hormone therapy offers adults with GHD significant benefits. In addition, the treatment guidelines for adults with growth hormone deficiency suggest:
- Adults who have had childhood GHD need to be retested after they reach full stature.
- Growth hormone therapy in adults improves cardiovascular health.
- Growth hormone therapy in certain adults with growth hormone deficiency may improve mortality rates.
- HGH therapy improves the quality of life of most adults with growth hormone deficiencies.
Conclusions That Can Be Drawn from the GHD Guidelines
In conclusion, all the guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of adult onset growth hormone deficiency all agree that, when the guidelines are followed, growth hormone therapy is a safe and effective treatment for adults with GHD. In addition the guidelines for adults with GHD conclude:
- Adult onset growth hormone deficiency is a well-recognized clinical entity.
- The prevalence of adult onset GHD in the population cannot be evaluated with any certainty.
- That HGH therapy is safe overall, however patients need to be carefully monitored for possible side effects.
- Growth hormone therapy provides body composition benefits.
- HGH replacement therapy improves bone health in patients with GHD.
- Growth hormone therapy reduced the risk of cardiovascular disease in adults with GHD.
- Growth hormone therapy improves the quality of life in adults with growth hormone deficiencies.
- The decision to prescribe HGH therapy should be based on individualized evaluation of the benefits vs the risks.
- Since the availability of recombinant growth hormone, many more people have been able to benefit from growth hormone therapy.
Remember, that the very definition of guidelines in medicine is to offer your doctor a set of suggestions based on evidence and best practices. Therefore, the decision to prescribe growth hormone therapy should only be made in part, based on these guidelines. Ultimately, the determination of whether you will benefit from growth hormone therapy, should only be made after careful consideration of your individual symptoms, needs and lifestyle.
The guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of adult onset growth hormone deficiency all agree that growth hormone therapy is a safe and effective treatment for adults with GHD.
read this next
What is the Best Age to Start Growth Hormone Treatment?
Human growth hormone or HGH plays a vital role in every stage of life. Growth hormone deficiency (GHD) is a medical condition that can…read moreGrowth Hormone Therapy
Growth hormone replacement therapy is a clinically proven method used to treat adults and children suffering from some form of growth hormone deficiency, or…read moreWhat Tests are needed before Growth Hormone Treatment?
Before you can start any kind of growth hormone treatment you must have your growth hormone levels tested. Legitimate growth hormone therapy can only…read moreWhat You Need to Know About Growth hormone Injections
There are many myths and misunderstandings about human growth hormone, or HGH. Here are some of the facts you need to know about growth…read more - Growth Hormone Therapy