- Home
- Growth Hormone
- Growth Hormone
- Growth Hormone Deficiency
- Growth Hormone Therapy
- Growth Hormone Injections
get startedThe Most Effective Hormone Replacement TherapiesWhat Does Human Growth Hormone Do
- Human growth hormone may very well be the most important hormone produced by the human body.
- Human growth hormone, or HGH, stimulates and regulates the growth and lifecycle of just about every cell of your body.
- In terms of biological function, HGH triggers protein synthesis and stimulates lipolysis, or the burning of fat into energy.
Human growth hormone may very well be the most important hormone produced by the human body. It is produced by the pituitary gland. Human growth hormone, or HGH, has many important functions. As you might be able to discern from its name, HGH is responsible for growth in children, but HGH has many critical functions in the human body even once you have grown beyond the time of puberty.
Once you are fully grown, your bone plates are fused, so HGH in adults does not cause you to keep getting bigger or taller, but it has a significant role in almost all major bodily processes and chemical reactions. In fact, you could say that the growth hormone produced by your pituitary gland actually keeps you alive by keeping your cells growing and dividing. As an adult, HGH is the primary source of energy responsible for regulating all of the complex processes that keep the biological machine that is your body functioning normally.
In children, HGH is responsible for growth. As an adult, HGH is primarily responsible to regulate all of the processes that keep the biological machine that is your body healthy and functioning normally.
Growth Hormone Function in the Human Body
HGH is a hormone. That means that, like all hormones, it is one of your body’s chemical messengers. The technical or biological term for growth hormone is somatropin. Somatropin is an endocrine hormone produced by the pituitary gland in response to stimulation from the hypothalamus.
HGH plays a critical role throughout your life by stimulating and regulating the growth and lifecycle of just about every cell of your body. Therefore, HGH is vitally important to build muscle and bone and to prevent poor growth in children. Throughout your childhood, as you continue to grow and mature, your levels of HGH rise progressively, eventually peaking around puberty when the most radical growth spurts and physical changes take place. However even once your growth plates fuse and you are no longer growing, human growth hormone continues to play a significant role in your health and well-being.
The technical or biological term for growth hormone is somatotropin. HGH stimulates and regulates the growth and lifecycle of just about every cell of your body.
The technical, or biological term for growth hormone is somatotropin. HGH stimulates and regulates the growth and lifecycle of just about every cell of your body.
Where Is HGH Produced?
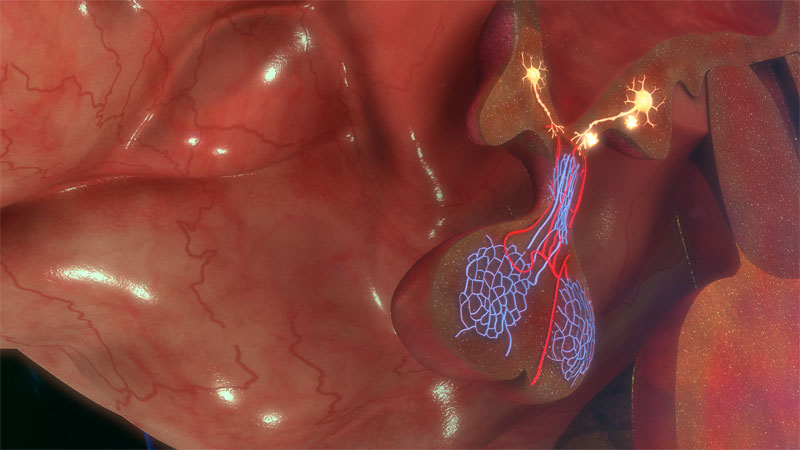
Growth hormone is primarily produced and secreted by one of the most important glands of your endocrine system, the pituitary gland. The pituitary is a small, pea-sized endocrine gland located at the base of your brian. It does not produce and release growth hormone continuously. Rather, it is released in bursts depending on the time of day, usually every 3 to 5 hours. This is why when you are tested for a possible growth hormone deficiency, doctors cannot merely take a sample of your blood and see if you have enough because you could be between bursts of HGH. Instead, to test for a growth hormone deficiency, doctors do what is called a growth hormone stimulation test. In this kind of test, the pituitary gland is induced to release a pulse of HGH, and then your blood is tested to see if the gland released the right amount of growth hormone for your size, weight, and age.
What Does HGH Do?
So what does HGH do, and exactly how does growth hormone increase cellular replication and thus allow for growth in size?
In terms of anatomic structure and function, HGH triggers protein synthesis and stimulates lipolysis or the metabolization of fat into energy. If you think of growing as a construction crew erecting a new building, basically, those are the "raw materials" needed for tissue growth – protein to provide the building blocks and energy to provide the labor.
The exact mechanism of action of growth hormone is not 100% understood. However, we do know that it does not act directly on the tissue it is “telling” to grow. Rather, it stimulates the liver and other organs to produce and release another hormone known as insulin-like growth factor 1, or IGF-1. IGF-1 and similar compounds are the chemical messengers that actually cause cells to grow. Much like growth hormone itself, once you have reached puberty and achieved your full normal body structure, your levels of IGF-1 significantly decrease. This is the built-in mechanism that stops excessive growth once you have reached your genetically predisposed full height.
However, as HGH and IGF-1 levels continue to drop as you grow older, you can start to feel the reduced strength and energy typical of “growing old.”
What Does HGH Do for Males?
The most important thing that HGH does for males is its impact on strength, weight, muscle growth, and body fat. Men with lower-than-normal levels of HGH and who are experiencing age-related growth hormone deficiency are far more likely to be obese. This is because the less HGH men produce, the slower their metabolism and the less efficient their body becomes at breaking down fat. One of the reasons that men tend to develop a “dad bod” as they age is because of age-related HGH decline. Men with age-related growth hormone deficiency are far more likely to be obese because the less HGH men produce, the slower their metabolism and the less efficient their body becomes at breaking down fat. In fact, one of the most obvious symptoms of GHD in males is being overweight, particularly having an excess amount of belly fat.
Growth hormone therapy is great for weight loss in men because it both improves metabolism and helps the male body build lean muscle. More lean muscle further increases your metabolism because even at rest, muscles crave energy. However, the way that HGH helps men get rid of extra weight, particularly around the middle, is that it improves lipolysis, which is your body’s ability to break down stored triglycerides into free fatty acids, or put more simply, to "burn fat."
The positive impact that human growth hormone has on metabolism can also lower blood pressure and blood sugar which lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease and other obesity-related conditions like diabetes.
In addition to enhancing your body’s ability to break down fats, HGH also helps you to lose weight by stimulating the release of more Insulin-like growth-factor-1 (IGF-1). Men, especially men over 40, who are obese tend to suffer from “insulin resistance.” When you have insulin resistance, insulin does not perform as efficiently, and therefore, you have higher blood sugar and more fat gets stored instead of converted to energy. IGF-1 fights insulin resistance by helping to move more glucose out of your bloodstream and into your cells. This will give you more energy, reduce your risk of diabetes, and help you to lose weight.
The collective impact of HGH helping men lose weight and build muscle also reduces their risk of heart disease. HGH in men can also improve athletic performance and sexual health.
What Does HGH Do for Females?
HGH in females has many of the same fat burning and muscle building effects as it does in males, however it also plays important roles in fertility and in bone health in women.
HGH has a multifaceted role in female reproductive health. It directly influences ovarian function, oocyte (egg) maturation, and the production of estrogen and progesterone. Optimal HGH levels are essential for the normal functioning of the reproductive system, including the menstrual cycle and the ability to conceive. In women, HGH acts as a regulator of ovarian function, promoting the growth and development of follicles, which contain the eggs. It facilitates the maturation of eggs within the follicles and their release during ovulation. HGH also promotes the production of healthy, mature eggs, increasing the chances of successful fertilization and implantation.
In females, HGH also interacts with other hormones, such as insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and insulin, to maintain hormonal balance. This equilibrium is crucial for regulating the menstrual cycle and preparing the uterus for pregnancy.
Just as in men, as women age, HGH levels naturally decline. This decline in HGH production can contribute to age-related fertility decline, as it affects egg quality and the regularity of the menstrual cycle. As in men, low levels of HGH due to age-related HGH decline can affect sex drive and sexual health in women and concurrently negatively impact conception. Increasing a woman’s growth hormone level with HGH injections can alleviate these issues along with additional benefits.
What Does HGH Do for Bone Health in Woman
HGH plays an important role in bone health, particularly in women who are far more prone to osteoporosis. Osteoporosis causes decreased bone density, which in turn is responsible for the weakening of bones that leads to fractures that are common among the elderly. Osteoporosis also makes these fractures difficult to heal, so osteoporosis fractures can be severely disabling to older women.
HGH has been scientifically proven to be able to prevent and treat osteoporosis. Many published studies have proven that HGH therapy can reduce or prevent osteoporosis fractures in older people. Postmenopausal women are most at risk of developing osteoporosis. HGH therapy has proven to be particularly useful in preventing fractures in this group of patients.
At the same time, as it is increasing your bone density, HGH also improves lean muscle mass. It is the body’s muscles that support and protect the bones from damage. Helping to build and strengthen muscle is another way that HGH works to prevent fractures in older women.
What Happens If You Do Not Produce Enough HGH?
In children who are not producing enough HGH, slow height growth is the result. Low HGH syndrome in adults is another matter entirely.
We all know that growing old brings with it a number of issues. The battery of symptoms that we think of as “aging”- loss of muscle mass, joint pain, weight gain, weakness, muscle pain, increased fatigue, sleep disorders, bone loss, loss of libido, and just an overall reduced sense of well-being – are collectively known to medical professionals as somatopause. Age-related decline of HGH is a direct cause of somatopause.
However, replacing this essential hormone through growth hormone therapy can replace the HGH that your body loses over time. By bringing your natural hormone well-beinglevels back into the normal range, growth hormone therapy can prevent many of the age-related diseases mentioned above, as well as improve overall health and well-being.
HGH is a powerful hormone. In adults with growth hormone deficiency, HGH replacement therapy has many positive long-term effects. HGH therapy can:
- Rejuvenate and invigorate every cell in your body
- Help you burn fat and decrease age-related muscle loss
- Increase exercise capacity
- Provide stronger bones
- Fight fatigue and give you more energy
- Reduce lines and wrinkles and provide you with a younger-looking face.
- Keep your moods more stable
- Lowers your risk of chronic kidney disease.
- Return you to more normal sleep patterns
- Improve sexual performance and sexual funtion
However, HGH deficiency in adults can only be diagnosed through a series of blood tests. If you are experiencing any or all of the symptoms listed above, and think you can benefit from the anti-aging effects of HGH, please see your healthcare professional to have your HGH levels tested.
What Is the Function of Growth Hormone Therapy?
Growth hormone replacement therapy involves injecting a synthetic form of HGH directly into the bloodstream. These synthetic forms of HGH come in many doses and brands, but they are all the same drug, a prescription medication known as somatropin.
If growth hormone is the fuel that your body runs on, it only stands to reason that once you remove that fuel, the engine slows and runs sluggishly. Do you ever look at kids running around on a playground? They seem to have boundless energy. That is because their HGH levels are very high. Have you watched those kids and ever said to yourself, “I wish somebody could bottle some of that energy?” Somebody has, and we call it, growth hormone replacement therapy. HGH therapy is designed to treat age-related GHD by returning your HGH levels to the healthy range.
However, do not be deceived by ads in magazines or online that claim to sell you products that contain HGH. You can only get real human growth hormone in an injectable form, and the only way to obtain such injections legally is with a doctor’s prescription. If you see an ad for a supplement or any product on a shelf that claims to contain “HGH,” and it can be obtained without a prescription or taken in any way other than an injection, it is not, by law, authentic HGH. Such products usually contain amino acids and other proteins that may raise your HGH level a bit, but they do not contain any HGH.
You could get a prescription for HGH from any physician. But you want to work with a specialist who not only understands the many functions of HGH in the human body but also the intimate relationship it has with your other hormones. You want to work with a clinic whose doctors are skilled and experienced in bringing all of your hormones into the proper balance for peak performance at any age.
Such practitioners, like ours with Kingsberg Medical, have extensive knowledge of antiaging medicine and provide adjunctive therapies to your HGH prescription that can help you not only increase growth hormone production but to be your best self, no matter your physical age.
So now that you know a little more about HGH and hormone replacement therapy, why not contact us and find out if you can benefit from growth hormone therapy? Or get started right now by filling out our medical history form!
The battery of symptoms that we think of as “aging”- loss of muscle mass, weight gain, weakness, increased fatigue, sleep disorders, bone loss, and loss of libido – are all a result of age-related growth hormone decline.
read this next
- Growth Hormone Therapy